
Let nature do the work
As a farmer you inevitably have a great impact on the soil. Therefore we should always farm in a way that benefits the soil.
Below we have collected facts and guides about how you, with relatively small actions, are able to ensure that your soils are treated well.
Soil water
The amount of plant-available water in the soil is determined by the diameter of the soil pores. It is important to avoid soil compaction, which causes pores to be compressed and reduces access to water. A loam contains approx. 20mm plant-available water per 10cm soil, but the amount that can be used by plants depends on root depth and root interweaving.
Early in spring after snowmelt or heavy rain, soil can reach its maximum water holdingt capacity, which means that all the pores are filled with water. As the soil dries out and water drains off, either naturally or with the help of subsurface drains, the soil reaches its field capacity.
Large pores empty
In this state of field capacity, the slightly larger pores are emptied of water and replaced with air, while the finer pores remain filled with water. The higher up in the soil profile the pores are, the more likely they are to be filled with air. In a soil with 50% solid material and 50% pores, at field capacity approx. 10-20% of the soil volume is filled with air and 30-40% with water.
Diameter decisive
The plant-available water present in pores in the soil is the difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point.
It is the diameter of the water-filled pores in (see table above) that determines how easy or difficult it is for plant roots to extract water from the soil. The pores in the soil are the result of its texture and structure.
| Water extraction force (‘root suction’) in metres of water column (mwc) |
Equivalent pore diameter (mm) |
|
|
Easily available |
1-6 | 0.03–0.005 |
| Available | 6-50 | 0.005–0.0006 |
| Slightly available | 50-150 |
0.0006–0.0002 |
| Unavailable | >150 |
< 0.0002 |
Kerstin Berglund, SLU
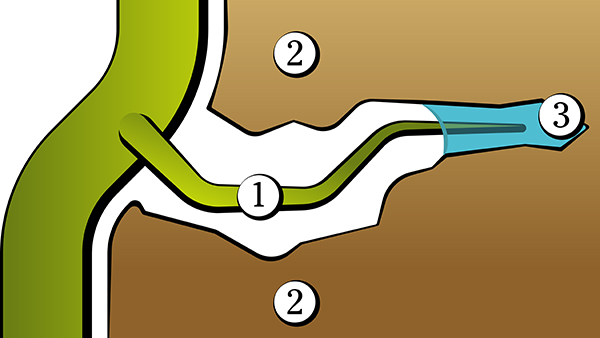
Root hair in pore
1) Root hair
2) Soil
3) Water
It is pore diameter that determines how tightly water is bound in the pores. The smaller the diameter, the more tightly water is bound and the harder it is for the root to extract it. Finally the root hair reaches its limit and can no longer extract water from the narrow pores.
The water in larger pores is easily available, but with decreasing pore diameter it takes progressively more energy by the plant to take up water according to image "Root hair in pore" above. The limit is at permanent wilting point, when root suction is no longer enough to extract water from the soil pores and the plant wilts. However, in practice plants cannot utilize all the water down to permanent wilting point, but give up long before.
Root depth decides
The amount of water that a crop can take up is decided by a combination of:
- The amount of plant-available water in (see table below)
- Root depth in the soil profile
- Root interweaving in the soil
| Soil type | Plant-available water (mm) per 10cm soil layer |
| Sand | approx. 10 |
| Silt | approx. 20–25 |
| Loam | approx. 20 |
| Clay brown | approx. 10–15 |
Source; Kerstin Berglund, SLU
Together, these three factors impose a type of biological wilting point. In this context, it is important for the farmer to know that soil compaction can impair water supply for the crop. If wheel slip compresses large pores in the soil, this impedes drainage and lowers the ability of the soil to supply plants with plant-available water.
Soil water management
The size of aggregates in the seedbed controls the amount of water that can evaporate. With an aggregate size of approx. 2mm, water evaporation is minimized. Straw at the soil surface also decreases water losses through reflecting solar radiation and preventing the soil surface from heating up.
If rain does not fall after sowing, the water present in and under the seedbed is critical for how well the new crop can establish. It is important to retain this water and manage it carefully if the seed is to germinate.
Sun heats up the soil
When the sun rises and begins to shine on a newly sown field, the energy from the sun’s rays heats up the water in and under the seedbed. Some of the water molecules acquire enough energy to convert to gaseous form and attempt to move out of the seedbed and into the air as water vapour.
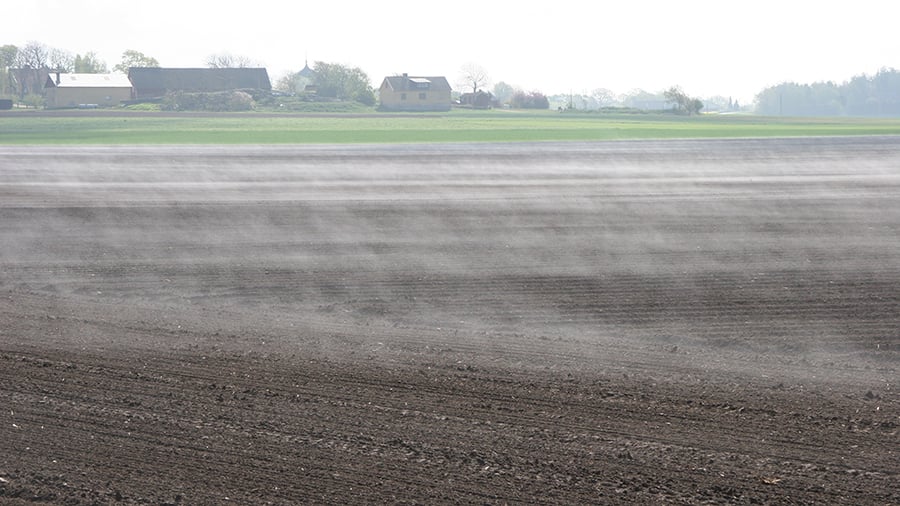

This evaporation of water can often be seen with the naked eye as wet soil is heated by the sun’s rays, as shown above.
In principle, this is the same phenomenon as when a saucepan of water boils on a hob and loses water in the form of steam.
Silt allows water losses
Evaporation of water from the soil surface after sowing is mainly controlled by the size of the aggregates in the seedbed.
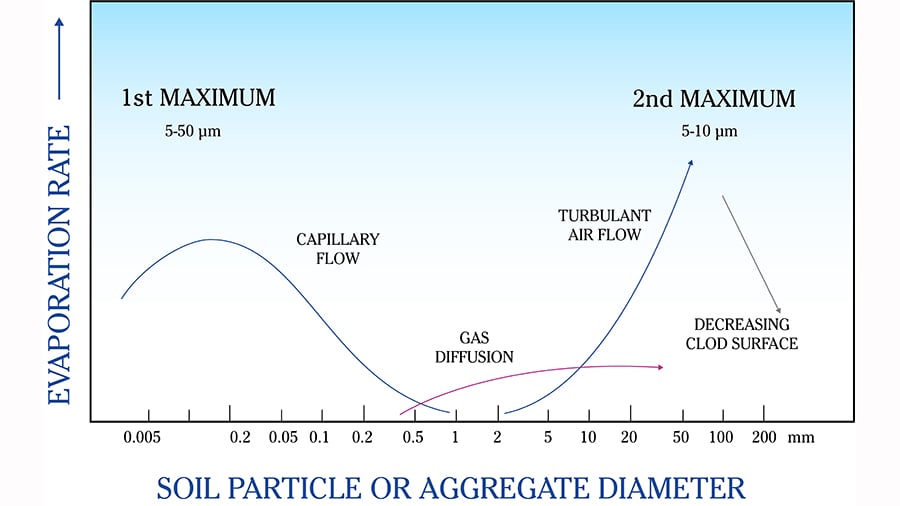
Figure below illustrates the fundamental relationship between water evaporation and soil particle/aggregate diameter. A first maximum in evaporation occurs at particle size 0.005-0.02mm. This is approximately the particle size area for silt and reflects capillary transport of water to the soil surface from the seedbed. On such silt soils it is important to interrupt capillary transport so that water is not lost.
Coarseness creates turbulence
A second maximum in evaporation rate is reached when the aggregate size exceeds 50mm, which is often the case in soils with high clay content. With such coarse aggregates in the seedbed, the air flows become turbulent and the seedbed dries out. Between these peaks, there is a minimum water evaporation case where the aggregates have a diameter of around 2mm. These aggregates are not small enough to permit capillary transport of water, but not large enough to create turbulent air flows. With aggregates of this size in a seedbed, a lid is put on and evaporation of water is minimized.
This can be demonstrated using pure aggregate sizes in a model experiment, see image. In other words, it is aggregate size that regulates evaporation of water from an open soil.

Winter wheat, 3 weeks after seeding
A: Aggregates < 2 mm give 95% emergence
B: Aggregates 2-5 mm give 60% emergence
C: Aggregates > 5 mm give 35% emergence
Straw reflects rays
Plant residues such as straw also affect the amount of water that evaporates from the soil. Straw at the soil surface affects water losses in at least two ways:
- The light-coloured straw reflects the sun’s rays, while the often dark-coloured soil absorbs solar energy
- The straw can interrupt upward capillary transport of water
Together, these two factors mean that the soil surface does not heat up as much in the spring and evaporation of water is restricted.
Reduced tillage can often reap the benefits of this effect. Better water retention in combination with better protection against erosion means that reduced tillage is the dominant tillage system in dry agricultural areas such as the prairies of Canada and the United States.
Earthworms
The digging done by earthworms leads to aeration and drainage of the soil. In addition, plant nutrients are released from harvest residues that have passed through the earthworms’ intestines. Farmers can encourage earthworms by supplying large amounts of organic material and by using less disruptive soil tillage.
In a normal soil on an arable farm, there can be between 100,000 and 1 million earthworms, with a combined weight of between 100 and 1000kg, within one hectare. These earthworms play a very important role in the soil when they carry out their work.
Through their activities they increase the drainage and aeration of soil when they open up channels for water and air down to the subsoil.


Porosity increases
In addition to their effect on drainage and aeration, earthworms also affect other soil physical properties of the soil. The number of pores increases and soil dry bulk density decreases when worms dig their way through the darkness of the soil. The soil tillage work carried out by the worms therefore greatly increases the number of macropores (diameter > 0.5mm) and creates a network of channels and spaces in the soil. This network can amount to 4000-5000km per hectare and the tunnels can extend to 2-3m depth. The tunnels act as ‘motorways’ for the roots in the soil. In a few years, earthworms move tens of tons of soil per hectare up to the soil surface as worm casts.
Accept Cookies to Continue
You need to accept cookies in order to view this feature. Click here to change your consent.
Better availability of nutrients
Soil biology is also improved, since the activity of earthworms stimulates microorganisms and actively spreads fungi and bacteria in the soil profile. This ultimately affects soil chemistry, since the availability of practically all nutrients is improved when organic material passes through the earthworm gut. For example, the concentration of nitrate is 8 times higher in worm casts than in the surrounding soil. These worm casts act as ‘glue’ between the soil particles, which improves aggregate stability and the soil structure.

Worms dislike tillage
Earthworms are sensitive to many components of modern agriculture, such as pesticides and soil compaction. Soil tillage is a sensitive issue, since it disturbs the worms and destroys their tunnel system. This is particularly true in September and October, when worm reproduction occurs. Soil tillage can be ranked according to the damage it causes to earthworms in the order: Direct seeding < tine cultivation < stubble cultivation < ploughing < rotavation.
The effect of the plough on worms is the subject of frequent debate. One study found that ploughing carried 10% of the total mass of earthworms in the soil up to the surface. Once there, birds ate around one-third, while two-thirds managed to escape and found their way back into the soil.


Food for the worms
To encourage earthworms it is important to feed them regularly. The best way to do this is to include a cover crop in the crop rotation. However, any measure that increases the amount of organic material in the soil is positive for the earthworm population. Green manuring and intercrops are therefore excellent worm feed.
In just a few years of a cover crop consisting of clover and grass instead of winter wheat, the number of earthworms in the following crop can be increased by 100%. Earthworms are therefore a good indicator of soil fertility. Where earthworms are thriving, crops will also thrive.
Roots
Roots live a secretive life under the soil. Under one hectare of winter wheat there can be 300,000km of roots supplying the crop with water and nutrients. Well-developed root systems are the result of good soil structure and is essential for high yield.
The roots anchor the plant in the soil and provide it with water and nutrients. The root system of a plant is usually just as genetically predetermined in terms of its shape and appearance as the leaves and stems above the soil. However, the environment in the soil (sand, clay, etc.) limits expansion of the roots. In a well-drained clay soil with good soil structure, the roots of certain plants can reach down to 2-3m.
Two different systems
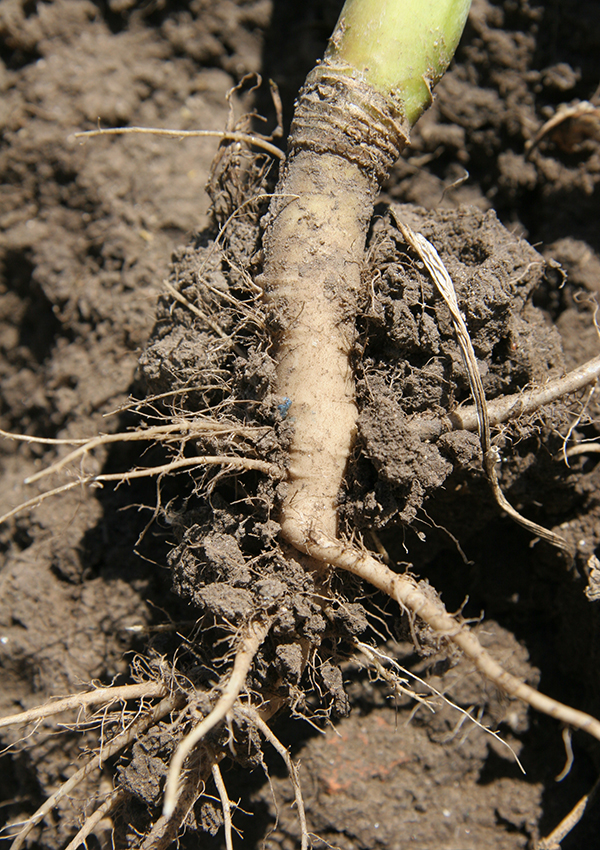

Dicotyledons, for example oilseed crops, have a root system consisting of a main root with side roots.
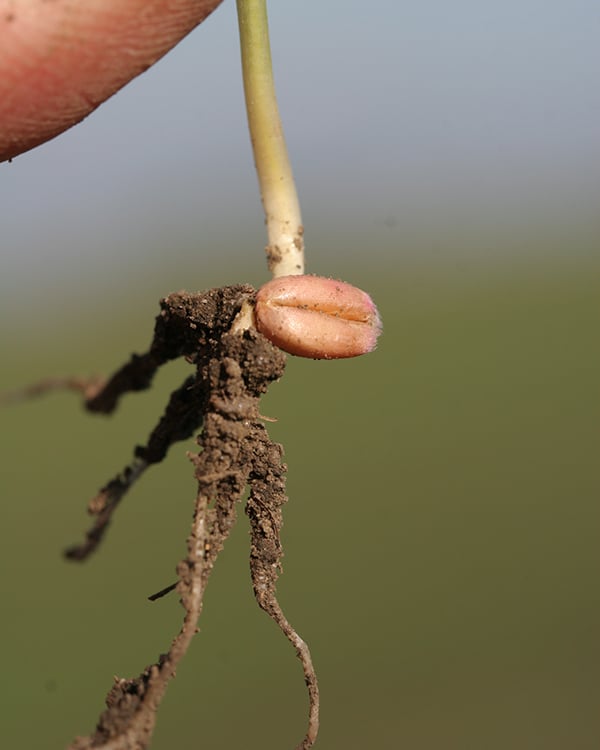

Monocotyledons, for example cereals, have 3-5 primary roots that come from the germinating seed and crown roots that are formed from the basal parts of the stem. Around 20-30cm behind a front of unbranched roots, the plant advances with a zone of very branched roots.
High speed but limited strength
Roots move through the soil profile at a rate of around 0.5-3.0cm/day in their period of fastest growth. However, the roots are dependent on cracks and holes in the soil for their growth, since their ability to create their own channels is rather limited. In a wet soil, the root tip can displace soil particles, but in a dry soil the roots are forced to use pores with a diameter that is greater than their own. Mechanical resistance in the soil is reflected by thickening of the root tip and branching. Roots and earthworms help each other in that the roots use worm tunnels and the earthworms use old root channels when they are moving through the soil profile.
Fine threads
Roots are very effective at taking up nutrients and water from the soil. At the very point of the root tip there is a root cap and behind this is the zone where the cells divide and elongate. Behind this, there is a zone with fine root hairs that have a diameter of around 0.01mm and a length of 1-10mm. These root hairs greatly increase the capacity of the root to take up water and nutrients. For example, a wheat root with a diameter of around 0.5mm can have an absorbing surface of 5cm2 per cm of root. The root hairs release mucus, which further increases the contact with the soil.
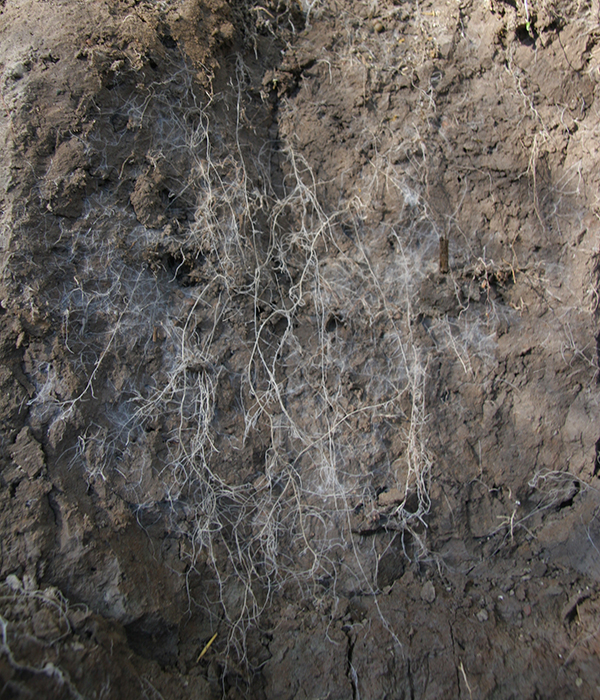

100m of roots in one litre of soil
The efficiency of the root system in taking up water and nutrients is a function of how well the roots can penetrate the soil; often measured as root length per cm3 of soil. In cereals it is common to find 10cm roots/cm3 soil in the topsoil, while the number decreases to 0.1cm roots/cm3 soil at 1m depth in the subsoil. This means that one litre of topsoil contains 100m of roots, while one litre of subsoil contains only 1m of roots at 1m depth in the soil profile. Root length per unit are is also amazingly high.
Anyone standing in one square metre of a sugar beet field has around 10km roots under their feet. Winter wheat has an even higher root density, with 30km roots per square metre. This means that one hectare of winter wheat is served by 300,000 km of roots under the soil surface.
Straw decomposition
Straw should be scratched and scraped by the combine harvester, so that the surface can be attacked more easily by soil microorganisms, and then rapidly buried in the soil enabling decomposition to get underway. When correctly managed, straw is an asset to the soil. Straw improves the soil structure and makes the soil more porous.

When straw is mixed into the soil, it is immediately attacked by fungi and bacteria. These micro-organisms need carbohydrates for their growth and use the straw as a carbon and energy source. This means that the weight of straw gradually decreases as microorganisms grow and break down the straw.
Weight decrease starts immediately
If straw stubble is mixed into the soil in the middle of September, it will have lost one-third of its weight by the middle of October. By the following spring, half the weight of straw will be left and in September, one year after it was first buried, only 10-20% of the original weight of straw will remain. The rest of the carbon will have become new bacteria and fungi, and have been lost to the air as carbon dioxide or will have formed new stable compounds of organic matter in the soil.
No need for extra nitrogen
During decomposition, the micro-organisms also need nitrogen. At the start of decomposition, the process therefore ‘steals’ some nitrogen from the soil and locks this out of the reach of plants. Around 3kg N per ton of straw is locked away during this period. When half the original weight of straw has been lost through decomposition, the process reverses and the nitrogen is returned to the soil. At that time, the levels of mineral nitrogen in the soil are sufficiently high and nitrogen deficiency due to straw decomposition seldom occurs. However, on headlands and patches that the combine harvester has missed there may be a lack of nitrogen, since large amounts of straw are accumulated there.
Abrasion is important

While the effect of tillage depth varies in terms of decomposition, it is important that the surface of the straw is scraped as it passes through the combine harvester. If not, the micro-organisms have problems attacking the organic structures on the surface of the straw.
‘Soiling’ the straw

Straw decomposition begins as soon as the straw comes into contact with the soil and the micro-organisms can start their attack. Decompositon is best in the top 5cm of the soil. The chop length of the straw is not as important for decomposition as long as subsequent stubble cultivation can take care of the straw. In a zero-till or minimum till operation, straw must be finely chopped to prevent residue buildup with the drill as well as crop emergence issues.
However, things start to happen even when the straw is lying on the soil surface. Three heavy showers of rain can result in the straw losing up to 90% of its potassium and 60% of its phosphorus content, which is leached back into the soil.

Straw decomposition increases fertility
The effects of regular mixing of straw with the soil, as opposed to straw burning, include better aggregate stability, more earthworms and a soil with higher porosity and higher hydraulic conductivity. Many farmers have observed this following the decline in popularity of stubble burning.
Dictionary:
Maximum water-holding capacity = all the pores are filled with water – as is the case below groundwater level or after snowmelt or persistent rain for example
Field capacity = free water has drained off down to a drainage depth of around 1m. This state is often referred to as drainage equilibrium, since water stops flowing in drains/ditches. In the soil profile above, the larger pores are filled with air at field capacity, while the finer pores still contain water
Permanent wilting point = when the water in the soil is bound with a water extraction force that exceeds 150m metres of water column (1500 kPa), the roots can no longer extract it. This limit is called permanent wilting point and represents water held in pores with a diameter that is less than 0.002mm
Texture = soil texture refers to the proportions of mineral particles with different average diameter, i.e. the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay in particular according to table "Particle size distribution" in chapter The building blocks of soil
Dictionary:
Subsoil = is that part of the soil profile that comes directly under the topsoil and is often unaffected by normal soil tillage to ploughing depth, but is sometimes tilled by deep loosening. The boundary between topsoil and subsoil is often clearly visible in ploughed soil as a plough pan, where plough shares and tyre slip have compacted the soil
Pores = are the spaces, channels and cracks in the soil, which are filled with either water or air depending on the actual water content of the soil.
Dry bulk density = is also called volume weight and refers to the weight of the soil in relation to its volume, including the air-filled spaces, once the soil has been dried to 105°C.
Worm casts = faeces/waste from the intestines, which in the case of earthworms is often visible as small heaps around the opening of worm channels at the soil surface.
Nitrate = plants normally take up the majority of the nitrogen they require as nitrate, NO3- which is a form of nitrogen that is found in the soil and also in mineral fertiliser. In the soil, specialist bacteria transform ammonium, NH4+, via nitrite, NO2- into nitrate. This process is called nitrification.
Dictionary:
Monocotyledons = plants that germinate from seed to produce a seedling with only one seed leaf (cotyledon), e.g. grasses and cereals
Dicotyledons = plants that germinate from seed to produce a seedling with two seed leaves (cotyledons), e.g. oilseeds, peas, beans, linseed, sugar beet, etc
Subsoil = the part of the soil profile that comes directly under the topsoil and that is often unaffected by normal soil tillage to ploughing depth, but is sometimes tilled by deep loosening. The boundary between topsoil and subsoil is often clearly visible in ploughed soil as a plough pan, where plough shares and tyre slip have compacted the soil
Dictionary:
Carbon dioxide = gaseous waste product (CO2) of cell respiration in the roots that is also the building brick together with water for sugars created by the plant through photosynthesis
Hydraulic conductivity = the amount of water that can infiltrate into the soil within a certain time is a good indicator of how well the soil is functioning from a soil physical perspective