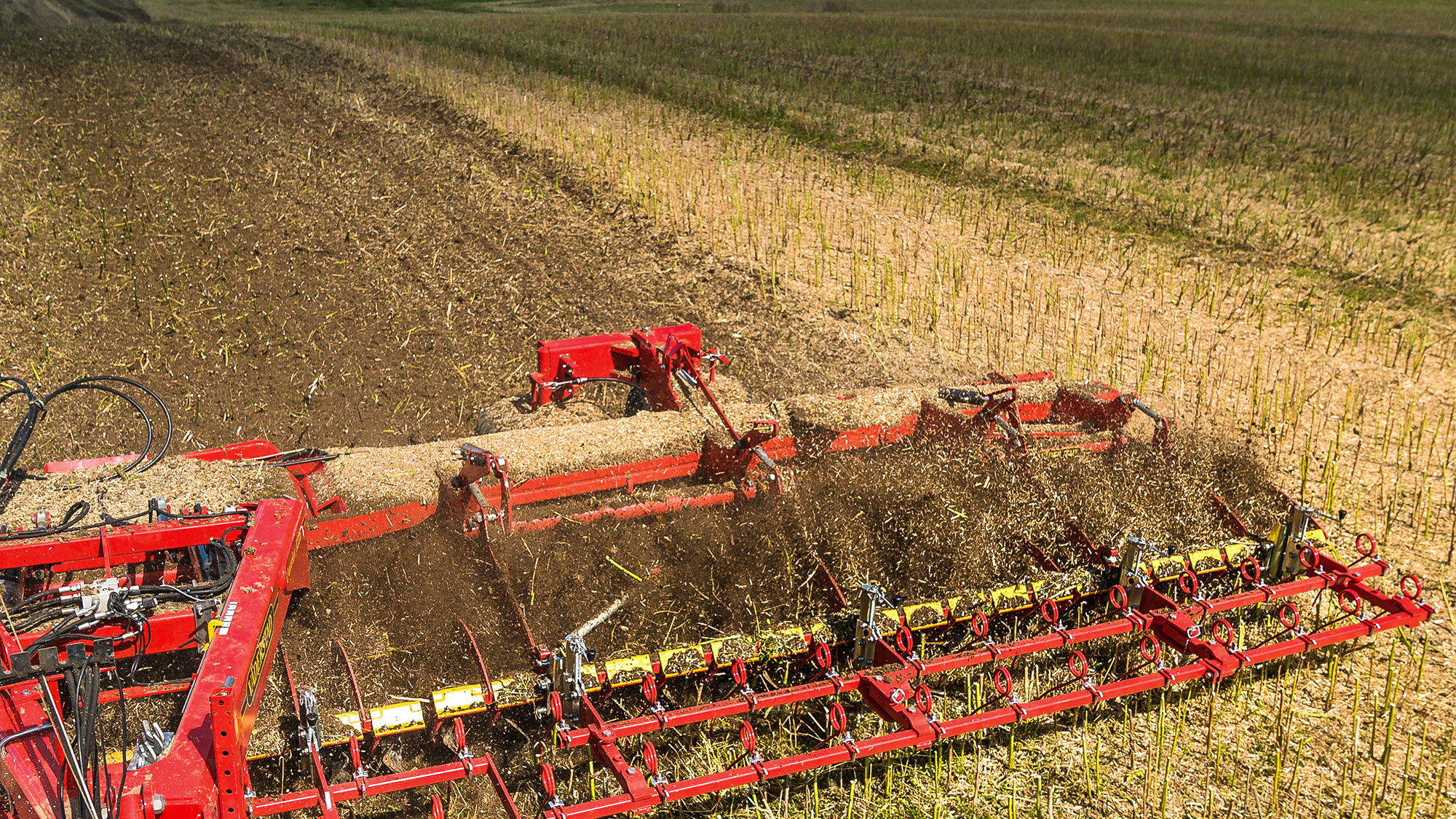
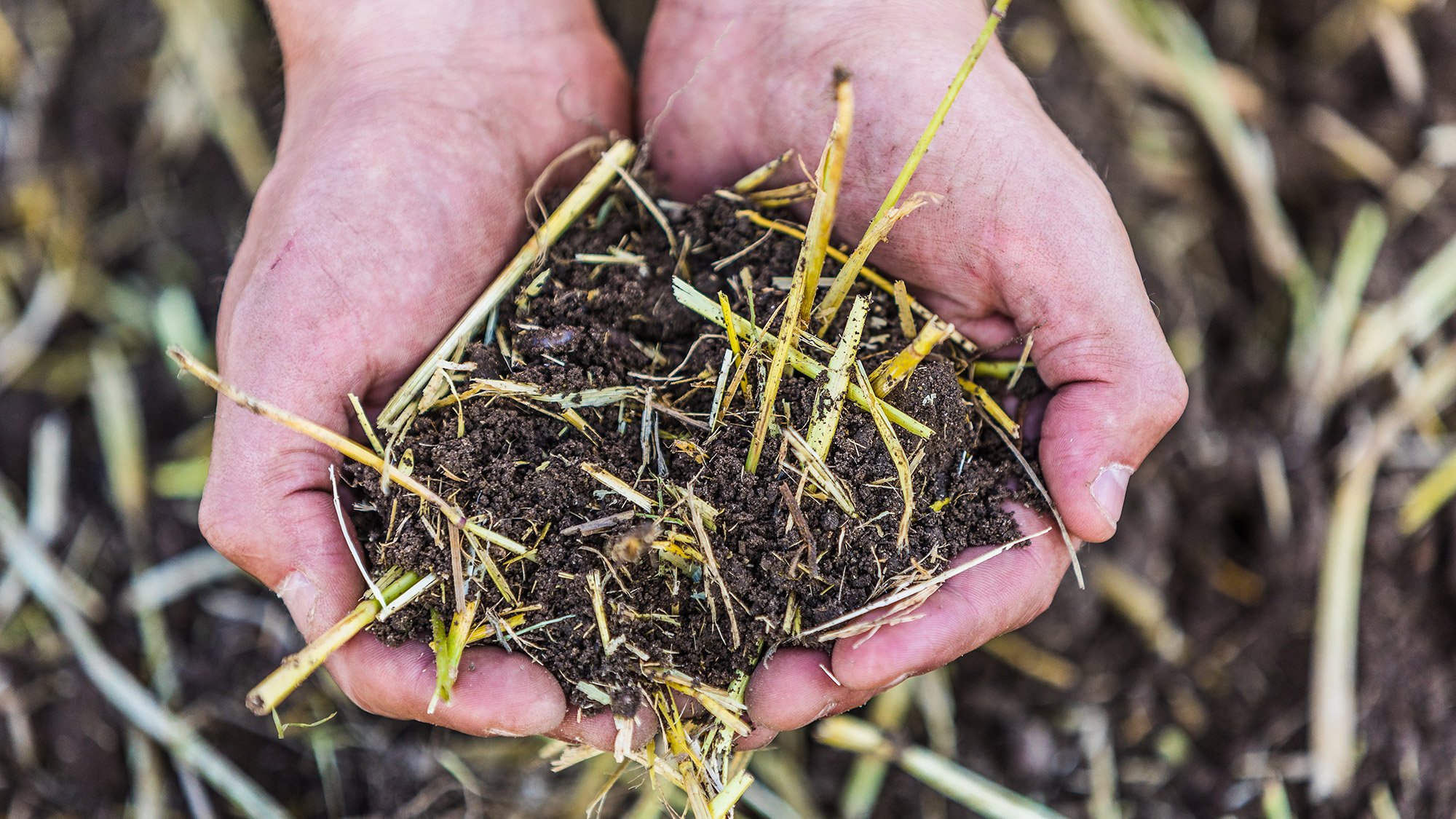
The rich stale seedbed
Many seeds and weeds are triggered by light. If buried too deep, they can stay dormant in the soil for many years. By providing a good seed-to-soil contact with access to light, ultra-shallow tillage makes sure the seeds will germinate into a stale seedbed when you want them to not years later. The extensive stale seedbed can later be eliminated with a second pass, to provide great field hygiene for the next crop.